Isotretinoin Impurities: Professional Solutions of Reference Standards for Pharmaceutical Companies and Research Institutions
Isotretinoin is a medication used to treat acne, particularly severe, cystic, and nodular forms of refractory acne. It improves acne symptoms by inhibiting sebaceous gland cell proliferation, reducing sebum secretion, normalizing abnormal keratinization of hair follicles, and suppressing the proliferation of Propionibacterium acnes. Additionally, it is indicated for other dermatological conditions such as pityriasis rubra pilaris and rosacea .
First approved in the United States in 1982, Isotretinoin saw increased market growth globally following patent expiration, with multiple companies launching generic or similar products. Rising patient awareness of dermatological treatments has further driven its market expansion .
However, Isotretinoin faces challenges due to serious side effects (e.g., teratogenicity, psychiatric risks) and high treatment costs. Regulatory restrictions are stringent: China’s Expert Consensus on Oral Isotretinoin for Acne Treatmentexplicitly endorses the safety of low-dose therapy (0.2–0.5 mg/kg/day) to mitigate risks .
As a critical drug for moderate-to-severe acne, Isotretinoin’s production and quality control are subject to rigorous regulatory standards. The Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2025 Edition)mandates that:
•Tretinoin content must not exceed 1.0% .
•The sum of other impurity peak areas should not surpass 1.0% of the main peak area in the reference solution .
•Limits for loss on drying, residue on ignition, and heavy metals are strictly enforced .
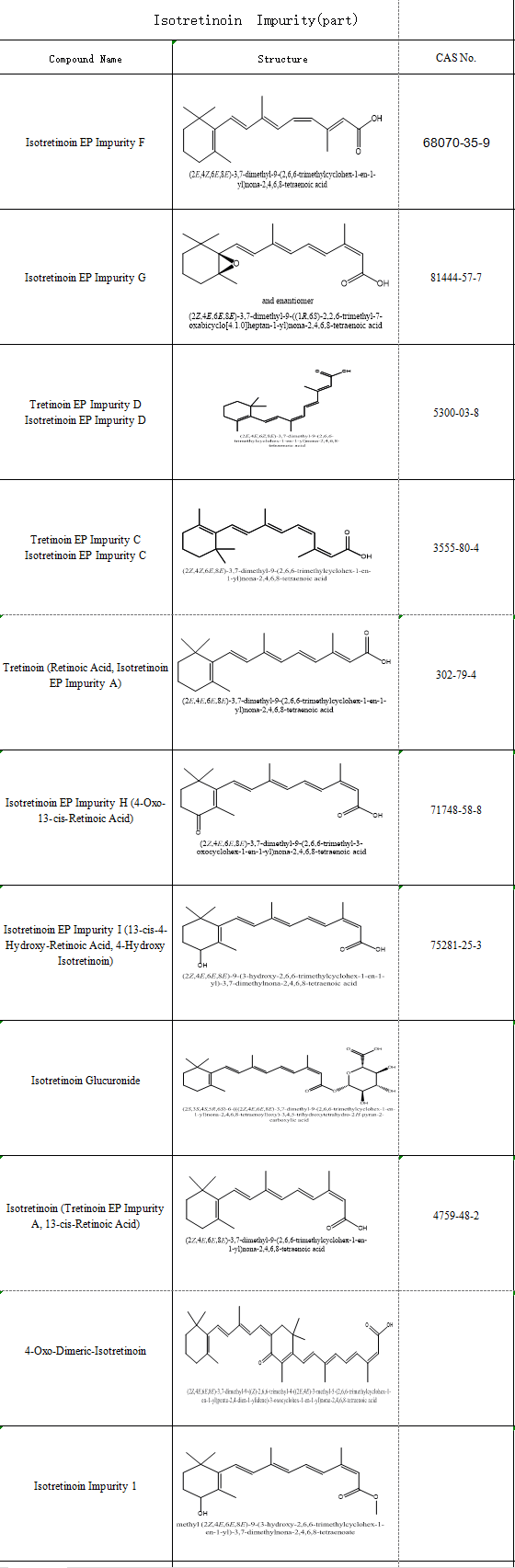
In pharmaceutical R&D, evaluating and controlling Isotretinoin impurities is essential for ensuring efficacy and safety. SZEB supplies a comprehensive inventory of Isotretinoin impurity reference standards, supported by full structural confirmation documentation compliant with EP/USP standards, facilitating regulatory submissions. For details, contact:
•Website: www.ex-biotech.com
•E-mail: sales@ex-biotech.com






.jpg) Wechat
Wechat